Describe the Motion of Particles in a Solid
310 describe the effects of changes in surface area of a solid concentration of a solution pressure of a gas temperature and the use of a catalyst on the rate of a reaction 311 explain the effects of changes in surface area of a solid concentration of a solution pressure of a gas and temperature on the rate of a reaction in terms of. This is made up of particles that are tightly or closely packed together such that they do not move pass each other but vibrates along a fixed axes.

The Particulate Nature Of Matter Igcse Cambridge 2019 2021 Teaching Resources States Of Matter Matter Science Matter Worksheets
The particles will gain energy and expand.

. When a solid turns into a liquid it is called melting. Particles are closely connected in a crystal lattice vibrate slightly on the spot-Has a definite shape and volume. In a solid the particles pack together as tightly as possible in a neat the particles are held together too strongly to allow movement from place to place but the particles do vibrate about their position in the structure.
7 Is the Sun Fire or plasma. Gas-vibrate and move freely at high speeds. Packed Tightly and Fast Motion.
When a liquid turns into a gas it is called evaporation. Solids-vibrate jiggle but generally do not move from place to place. Username E-Mail Password Confirm Password Captcha Giải phương trình 1 ẩn.
Use an audience in a movie theater to describe the motion of particles in a solid. Close Together and Slow motion. Heat makes the particles in a solid vibrate faster giving them more kinetic energy.
An insulated thermos contains 148 g of water at 727 c. When exposed to cold temperatures the particles lose energy and move more slowly. Describe the energy and motion of particles in a solid.
B A teacher uses this method to find the density of liquid nitrogen. Particles in solid are closely packed and vibrate at about a fixed point and have very strong forces of attraction between them. Describe the energy and motion of particles in a solid.
8 How will you describe the particles in solid the particles in solid are. 2 Use the kinetic particle model to describe the motion and separation of the particles in. Particles move rapidly in all directions and collide with each other more frequently.
The movement of particles in liquids are in a random motion. 2 liquid solid ii Describe the motion of the particles in liquid nitrogen. Start your trial now.
5 How are the particles of matter affect its states as to solid liquid and gas. The particles in a liquid are loose and can move past each other. 4 How the molecules in a solid liquid and gas compare to each other.
Solid carbon dioxide carbon dioxide gas. Matter that has a definite volume but no definite shape is a. Faster-vibrating particles bump into one another more often and hit each other harder.
When a substance freezes it changes from a. In liquids and gases the forces between the particles is weaker than forces between particles of solid. Particles can move all over the place spread far apart -Has no definite shape or volume.
The Particles in a solid gain so much energy that the vibrations increase and the particles break from the fixed positions. Liquid-vibrate move about and slide past each other. The particles in a solid are tightly packed together and create very little energy by vibrating How can you describe the motion of particles in a liquid.
The specific heat of liquid water is 4190 jkgk. And the heat of fusion of water is 333 kjkg. What happens to a substance during changes between liquid and gas.
The program should start with solid Neon. What is the net entropy change of the system from then until the system reaches the final equilibrium temperature. Packed Tightly and Vibrating in place.
Far apart and RapidRandom Motion. Describe the energy and motion of particles in a solid. Particles in a solid are tightly packedusually in a regular pattern.
9 How does the movement of particles change from solid to. First week only 499. Solution for Describe the characteristic movement of the particles of solid liquid and gas and arranged them in increasing motion of the particles.
Conversely the motion of the particles is reduced by lowering the temperature until at the absolute zero 0 K the motion of the particles ceases altogether. The motion of the particles is increased by raising the temperature. Particles in a solid are tightly packedusually in a regular pattern.
The vibrational motion of particles in solids is kinetic energy. A 0 The diagram shows the arrangement of. Describe the motion of particles in a gas and liquid when they are exposed to cold.
Explanationkasalipo yung naka jiggle apsiganocj and 39. Describe the motion of particles in a gas and liquid when they are exposed to cold. You put in a 117 g ice cube at 000 c to form a system of ice original water.
When a substance melts it changes from a solid to a liquid. 2 Use the kinetic particle model to describe the motion and separation of the particles in. X 2 - 2x 1 -x.
Measure the mass of a container pour. 6 How plasma is different from gas. Like solid particles the audience in a movie theater are close and in fixed positions but can still move.
Because the particles are in motion they will have kinetic energy. The particles in gases can move freely as the forces of attraction between particles are almost negligible. Hỏi x.
Particles roll over one another can move around some space between particles-Has a definite volume but no definite shape. Particles in solids are always vibrating moving back and forth in place. 1 This question is about liquid nitrogen.
Solid carbon dioxide carbon dioxide gas. Describe the spacing and motion of the particles in a solid. When exposed to cold temperatures the particles lose energy and move more slowly.
Particles in a solid can vibrate but not move past each other.

How Can You Describe The Motion Of Particles In A Solid How Can You Describe The Motion Of Particles In A Liquid How Can You Describe The Motion Of Particles Ppt

Arrangement Of Molecules In The Three States Of Matter States Of Matter Interactive Science Notebook Middle School Science Experiments
How Are Particles Arranged In The Three States Of Matter Quora

Phases Of Matter States Of Matter Solid Liquid Gas Matter Science

How Can You Describe The Motion Of Particles In A Solid How Can You Describe The Motion Of Particles In A Liquid How Can You Describe The Motion Of Particles Ppt

Difference Between Solid Liquid And Gas In Tabular Form States Of Matter Simplified Solid Liquid Gas States Of Matter Intermolecular Force
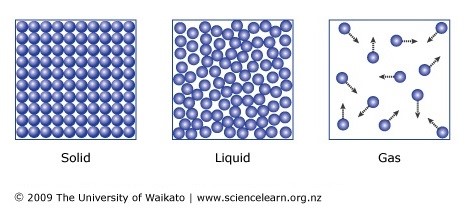
5 10 Describe The Arrangement And Motion Of Particles In Solids Liquids And Gases Tutormyself Chemistry

Motion Of Particles Flashcards Quizlet

David Chalk Teacherchalky1 Twitter In 2021 Gcse Science Revision Science Revision Gcse Science

Sci Challenge On Twitter Biology Revision States Of Matter Science Teacher

Physical And Chemical Changes Science Freebie Matter Science Matter Worksheets Science Worksheets

Solids Liquids And Gases Match And Draw Use This Activity To Match The Descriptions Of Solid Liquids Solid Liquid Gas Science Worksheets Matter Worksheets

How Can You Describe The Motion Of Particles In A Solid How Can You Describe The Motion Of Particles In A Liquid How Can You Describe The Motion Of Particles Ppt

Image Result For Carroll Venn Diagrams Statements Venn Diagram Activities Venn Diagram Matter Science

This Lesson Is Designed For The New 2019 2021 0653 Igcse Combined Science Course The Presentation Contains States Of Matter Matter Science Matter Worksheets

8 Kinetic Model Of Matter Content States Of Matter Brownian Motion Kinetic Model Solid Liquid Gas Science Blog Physics Lessons

Arrangement Of Particles In Phases Of Matter Comparison Expii

Comments
Post a Comment